Aspartic Acid at Ph 3
The first category of acids are the proton donors or BrønstedLowry acidsIn the special case of aqueous solutions proton donors form the hydronium ion H 3 O and are known as Arrhenius. The ionic form is known as aspartate is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
Any of various typically water-soluble and sour compounds that in solution are capable of reacting with a base to form a salt redden litmus and have a pH less than 7 that are hydrogen-containing molecules or ions able to give up a proton to a base or that are substances able to accept an unshared pair of.
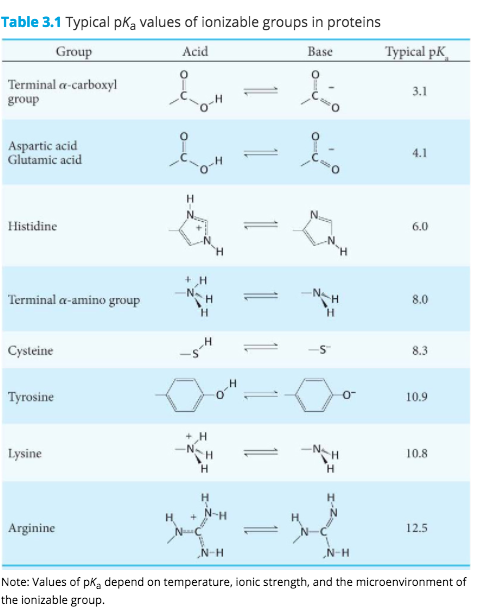
. 39 mg in 100 mL. In 2004 Rawlings and colleagues introduced a classification of protease inhibitors based on similarities detectable at the level of amino acid sequence. The isoelectric point pI pHI IEP is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean.
Diets that meet or exceed the RDA for total protein 08 gkgday. Asparagine symbol Asn or N is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteinsIt contains an α-amino group which is in the protonated NH 3 form under biological conditions an α-carboxylic acid group which is in the deprotonated COO form under biological conditions and a side chain carboxamide classifying it as a polar at physiological pH. In most acid stable proteins such as pepsin and the soxF protein from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius there is an overabundance of acidic residues which minimizes low pH destabilization induced by a buildup of positive charge.
56 grams for a 70 kg person meet or exceed the RDAs for branched-chain amino acids. A branched-chain amino acid. È coinvolto anche nel ciclo dellurea ed è inserito fra gli amminoacidi gluconeogenici in quanto per transamminazione si trasforma in ossalacetato.
Sds_3953 Hydrochloric Acid Solution Less than 01 M. An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group NH 2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid. Its α-amino group is in the protonated NH 3 form under physiological conditions while its α-carboxylic acid group is deprotonated COO under physiological.
434 mg in 100 mL. This classification initially identified 48 families of inhibitors that could be grouped into 26 related. HCO 3 CO 3 2 H K a2 469 10 11 molL.
Protease inhibitors may be classified either by the type of protease they inhibit or by their mechanism of action. At high pH it dissociates significantly into the carbonate ion CO 3 2. Contains no more than.
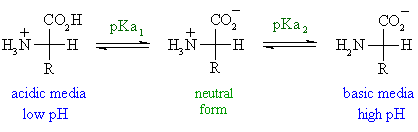
Fatty acid synthase FASN EC 23185 is a multienzyme that catalyzes the conversion of acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA to the 16-carbon fatty acid palmitate. In sufficiently acidic environments the amino group gains a proton and the molecule becomes a cation with a single positive charge HOOCCHNH 3CH 2 2 COOH. It is considered to contain a strong umami taste.
FASN overexpression and hyperactivity is commonly associated with malignant cells. The term amino acid is short for α-amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid. Vmax440 nmolminmg enzyme for the oxidation of NADPH at pH 70 ECO0000269PubMed.
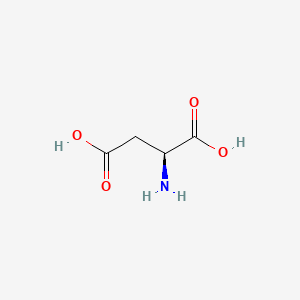
The electrophoretic linear. When glutamic acid is dissolved in water the amino group NH 2 may gain a proton H andor the carboxyl groups may lose protons depending on the acidity of the medium. Aspartic acid symbol Asp or D.
The pH usually measured by potentiometry with a cell comprising a glass electrode and a combined reference electrode is strictly defined as -log a H see definition of pH where a H is the activity of hydrogen ions more precisely hydrated protons H 3 O or hydronium the simplest type of oxonium ion. Molecular weight of the amino acid residues. The peptide net charge calculator at a given pH is based on the formula below.
Hydrogen ion H known as a BrønstedLowry acid or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair known as a Lewis acid. Soy sauce in its current form was created about 2200 years ago during. The buildup of which can lead to metabolic acidosis with pH levels as low as 64.
This difference can be attributed to the conversion of asparagine and glutamine into aspartic acid and glutamic acid respectively during the basic reaction. Combined with methione and aspatic acid thronine also helps to process fatty acids and prevent liver failure. The isoelectric point of gelatin A is in the region of pH 9 while it is about pH 5 for gelatin type B.
20 mg of Threonine Female 1200 mg. ASPARTIC ACID ASPARTIC ACID ASPARTIC ACID. One study found that when men took D-aspartic acid and weight trained for 28 days they experienced a 29-pound 13-kg increase in lean mass.
L-Tyrosine or tyrosine symbol Tyr or Y or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteinsIt is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side groupThe word tyrosine is from the Greek tyrós meaning cheese as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. Sds_3951 Hydrochloric Acid Solution 25 M - 59 M. However those in the placebo group experienced a.
Good sources of this essential amino acid include meat grains dairy leafy vegetables and mushrooms. For the molecular weight amino acid calculator you can enter the 1- or 3- letter code of the desired amino acid and the tool will provide the value the same way it would calculate peptide molecular weight. All biological tissues contain amino acidsAll amino acids except glycine.
In organisms carbonic acid production is catalysed by the enzyme carbonic. An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton ie. Other mechanisms include minimization of solvent accessibility of acidic residues or binding of metal cofactors.
Methionine abbreviated as Met or M. This technique relates changes in amino acid molecules to the time elapsed since they were formed. PH 56 52-60 adjusted with acetic acid.
Encoded by the codon AUG is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteinsIt contains a carboxyl group which is in the deprotonated COO form under biological pH conditions an amino group which is in the protonated NH 3 form under biological pH conditions located in α-position with respect to. Each molecule contains a central carbon C atom called the α-carbon to which both an amino and. Like all other amino acids it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid.
At higher pH pH 9 and positively charged at lower pH pH 5. Isoleucine symbol Ile or I is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteinsIt contains an α-amino group which is in the protonated NH 3 form under biological conditions an α-carboxylic acid group which is in the deprotonated COO form under biological conditions and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch a central carbon atom bound to three. PK a2 10329.
Amino acid dating is a dating technique used to estimate the age of a specimen in paleobiology molecular paleontology archaeology forensic science taphonomy sedimentary geology and other fields. Sds_4059 PolySnow sds_4105 Iodine-Potassium Iodide Electrolyte Solution. The meaning of ACID is a sour substance.
13 and 17 gday. Soy sauce also called simply soy in American English and soya sauce in British English is a liquid condiment of Chinese origin traditionally made from a fermented paste of soybeans roasted grain brine and Aspergillus oryzae or Aspergillus sojae molds. Male 1600 mg per kilo per day.
Basic while a protein with an excess of acidic aminoacids aspartic acid andor glutamic acid will often have an isoelectric point lower than 7 acidic. The bicarbonate ion is an amphoteric species that can act as an acid or as a base depending on pH of the solution. Lacido aspartico è un amminoacido utilizzato degli esseri viventi per la sintesi delle proteineViene indicato comunemente con le sigle D o Asp ed è codificato sullRNA messaggero dai codoni GAU e GAC.
151 mEqL including quantity used for pH adjustment.

Solved 3 For Aspartic Acid At Ph 7 What Is The Ratio Of Chegg Com
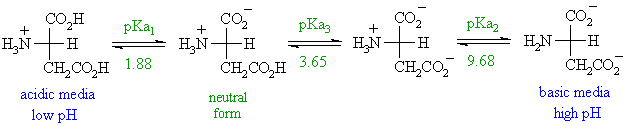
0 Response to "Aspartic Acid at Ph 3"
Post a Comment